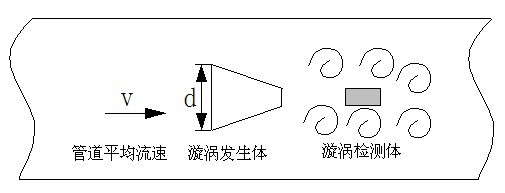
Vortex Flowmeter Fault Analysis and Treatment Measures First, vortex flowmeter measurement principle The basic principle of the vortex flowmeter is the phenomenon of Karman vortex street. The vortex street is generated alternately on both sides of the vortex generating body and forms a vortex street downstream of the main body (as shown in the figure). The frequency of the vortex separation is proportional to the flow velocity and inversely proportional to the width of the vortex generator. It can be expressed by the following formula: F=St·V/d ············ Where: F - vortex separation frequency St - dimensionless constant (Stauhal) V - Velocity of the vortex generator D—the width of the inflow surface of the vortex generator By measuring the separation frequency of the vortex, the fluid flow rate and instantaneous flow rate can be measured. The Strouhal number St is a dimensionless constant that can be experimentally determined. The linear part of the relation between the dimensionless constant St and the analogous No function is the linear measurement range of the vortex flowmeter. When the frequency F is detected, the velocity of the fluid in the tube can be obtained, and then the volumetric flow rate can be obtained from the flow velocity. The ratio of the number of pulses output over a period of time to the volume of the fluid (the number of pulses flowing through a unit volume of fluid) is called the meter coefficient (K-factor). K=N/Q ·········· Formula (2) Where: K—meter factor (pulse/M3) N-pulse number Q—fluid volume (M3) The vortex separation frequency used to measure the flow rate varies with the flow rate and is not affected by the fluid density and viscosity. The pressure pulsation generated by the vortex separation is detected by the pressure sensitive sensor and converted into a pulse signal corresponding to the vortex frequency in the detection circuit. The signal converter converts this pulse signal into a 4-20 mA standard current signal output. Second, install 2.1 Installation Instructions The vortex flowmeter can be installed outdoors or outdoors. The flowmeter is best installed in a place where the vibration is small to prevent the vibration from affecting the accuracy of the measurement. When the pipeline vibration is large, the pipe should be installed and supported; if the pipe is always full of the measured medium. Liquids, then the pipe can be installed vertically or at any angle; the inner diameter of the flowmeter's connecting pipe must be slightly larger than the inner diameter of the vortex meter, within the range of (1-10mm). Ideally, an energy storage device can be installed upstream of the flow meter, which can reduce the vibration of the liquid and improve the measurement accuracy. 2.2 Reducing tube, expanding tube, bending tube Corresponding to the shrink tube, it is necessary to ensure that the length of the straight pipe section measured upstream should be at least 25D, and the length of the straight pipe section measured downstream should be at least 5D; corresponding to the pipe expansion, the length of the straight pipe section measured upstream should be at least 25D. The length of the straight pipe section measured downstream shall be at least 5D. Corresponding to each section of the elbow, it must be ensured that the length of the straight section measured upstream of it should be at least 25D, and the length of the straight section measured downstream should be at least 5D. (D: nominal internal diameter of vortex flowmeter) 2.3 valve positioning and pipe length and temperature measurement pressure point selection (1) The valve should be installed downstream of the flowmeter. The length of the upstream straight pipe segment depends on the upstream pipe condition (such as shrinkage pipe, pipe expansion, elbow pipe, etc. The length of the downstream straight pipe segment should be at least 5D. (2) If the valve Must be installed upstream of the flowmeter, then ensure that the length of the straight section upstream is at least 50D, and the length of the straight section downstream should be at least 5D. When pressure measurement is required, set the pressure measurement point upstream of the flowmeter 1D-3D Between the place; temperature measurement, the temperature measurement hole set in the downstream 3D-5D of the flowmeter. 2.4 Effect of Pulsating Flow on Flow Measurement Fluids may vibrate strongly on high pressure liquid lines using piston or roots blowers or air compressors or high-pressure liquid lines using piston or column pumps. Usually, the valve should be installed upstream of the flowmeter. If you have to install the flowmeter upstream of the valve, you can install a pulsating flow attenuator upstream of the flowmeter, such as a throttle plate or expansion fracture, in the use of T-type In pipelines, the valve is installed in front of the flowmeter to avoid pulsation pressure fluctuations, leading to zero fluctuations of the instrument. Third, failure analysis and treatment measures 3.1 Pipe Flow Meter No Output phenomenon the reason Testing methods Treatment measures Pipe flow meter without output Instrument no display no output 1, power failure Detect the power supply voltage with a multimeter Re-power or replace the power 2, the power supply is not connected Detect the power supply voltage with a multimeter Power on 3, the connection cable is broken or the wrong line Check if the line is unblocked Reconnect and check the cable Instrument shows no output 1, the flow rate is too low, did not enter the measurement range Increase the flow to see the display Increase flow or reselect flow meter 2, a certain level of the amplifier board is faulty Check with other type of flowmeter board replacement at the site Replace the motherboard 3, the probe body has damage First, increase the flow rate, replace the vortex motherboard with the same type of vortex street, if you exclude the motherboard failure, check the probe signal Replace the probe 4, the pipeline is blocked or the sensor is stuck If all of the above reasons, please check the installation of pipelines and meters Reinstall the instrument 3.2 No flow after power on but output phenomenon the reason Testing methods Treatment measures No flow after power on but output The output signal is stable 1, the output frequency of 50 Hz power frequency interference Use a multimeter to check the frequency Use shielded cable to reconnect according to regulations 2, the output frequency is any constant frequency or constant output current value (damage of the amplifier board, resulting in self-excitation) Check whether the output current of the main board is a constant value or the pulse is a constant value Replace the amplifier Output signal changes 1. Strong flow devices or high-frequency interference near the flowmeter Check if there is such equipment around Reselect installation location 2, the pipeline has a strong shock Feel the concussion of the pipe by hand Reinforces the piping of the flowmeter installation section 3, amplification board amplification or trigger sensitivity is too high Commission GB and SB check output signal Counterclockwise Decrease Magnification (GB) or Sensitivity (SB) 4, the pipeline valve is not completely closed, there is leakage flow Check pressure and valve closure Check valve 3.3 Unstable flow output phenomenon the reason Testing methods Treatment measures Unstable flow output Selection installation is extremely piping reason 1, there is a strong electrical interference signal, the instrument is not grounded, flow and interference signal superposition Check ground Reconnect 2. Insufficient straight pipe section or inner diameter of the pipe is inconsistent with the inner diameter of the meter Check the inner diameter of the pipe and the inner diameter Replace the installation position again 3, the impact of pipeline vibration Feel the concussion of the pipe by hand Reinforce pipes to reduce vibration 4, flow meter installation of different hearts Remove the instrument to check the position of the flange and pipe Reinstall the instrument 5, the fluid is full Check fluid flow conditions extremely instrument installation position Reinstall the instrument 6, the flow rate is lower than the limit or exceed the upper limit Check fluid flow and gauge range Increase the decrease flow or adjust the amplification board filter parameter K1 K2 K3 7. There is cavitation in the fluid Check fluid condition Install downstream valve on the instrument to increase back pressure Instrument reason 1, the instrument menu settings are wrong Check the instrument menu settings Re-set the menu as required 2, the motherboard is damaged Replace the motherboard to check if the flow shows no change Replace the motherboard 3.4 Meter Display Flow and Process Flow Do Not Match phenomenon the reason Testing methods Treatment measures The meter display flow does not match the process flow Instrument reason 1, the flow meter failed to work Check meter settings Re-installation requirements set and refer to the three treatment methods 2,4-20mA full-scale setting error Check the full scale setting According to the actual amount according to the instructions to reset the full range Selection design reason 1. The measurement gas or steam is not compensated in real time or fixed temperature pressure is set to compensate Check the temperature compensation element and its settings Add a warm pressure compensation element or set a fixed value compensation 2. Measuring gas or steam temperature measuring pressure element installation method or installation position is incorrect Check the temperature compensation element and its settings Reinstall the temperature and pressure compensation components as required 3. The user accounts for the flow of the meter with the rated output of the equipment Check the rated output of the device Recalculate process flow 4, saturated steam is not saturated Check steam process Changing process conditions
The spring cone crusher has a perfect combination of
high-performance crushing chamber and high crushing frequency, which greatly
improves the crushing capacity. At the same time, it also absorbs the principle
of laminated crushing, which to a certain extent reduces needle like materials.
The spring safety system is an overload protection device that provides
"spring type" over iron release protection for foreign objects (iron
blocks). Under normal use, the equipment has a fault free operation rate of
over 95%.
Operational Principle:
The spring cone crusher uses a working surface between a movable
cone and a stationary cone to crush ore. The moving cone is supported on a
spherical bearing and fixed on a suspended vertical axis, which is placed
inside an eccentric sleeve, which in turn is placed on a thrust bearing. The
moving cone and the vertical shaft are driven by an eccentric shaft sleeve,
which is driven by a horizontal shaft and a belt pulley, and transmitted
through an bevel gear. The pulley is driven by an electric motor through a V-belt.
The lower part of the vertical axis is installed into the eccentric sleeve, and
when the eccentric sleeve rotates, a conical surface is drawn with the axis.
Therefore, when the moving cone approaches the stationary cone, the ore is
crushed. The casing consists of two parts, upper and lower, connected by bolts.
A strong spring is installed on the bolt to prevent damage to the crusher (such
as the spindle) when metal or other hard objects fall into the crushing
chamber. If a metal block or other hard object (nut, drill head, etc.) enters
the crushing chamber together with the ore, the stationary cone is lifted and
the ore discharge port increases to discharge it.
Compound Spring Cone Crusher,Cone Crusher,Spring Cone Crusher SiChuan TieYing Machinery Manufacturing CO.,LTD; , https://www.tieyingcrushers.com